|
Google Display Advertising is hands down one of the best options for marketers who want to reach out to a large audience. The Google Display Network can give you access to over 90% of all internet users, which is remarkable in itself. And, to top it off, it provides excellent targeting options to ensure that your ads are displayed only to a relevant audience.
With Google Display Advertising, you get complete control over who sees your ads, where, and how many times. And, the interface is easy-to-use and helps you optimize your Google Display Advertising campaigns, even if you are not an expert. In this post, we will tell you everything that you need to know about Google Display Advertising. Google Display Advertising: The Basics When it comes to things you need to know about Google Display Advertising, it’s best to start with the basics. Here are some of the basics of Google AdWords and Google Display Advertising. 1. What is the Google Display Network? This is a collection of over 2 million websites and apps where display ads from Google AdWords can be shown. So, if you use Google AdWords to run an advertising campaign, then your ads can be displayed on any or all of these websites and apps. This includes all of the products in the Google Suite, its affiliated websites, video-streaming websites like YouTube, and a lot more. 2. Why Use Google Display Ads? Google claims that the network can reach over 90% of all internet users in the world. This is much higher than what you will get if you use any other advertising platform. It also provides good targeting options, not just for reaching the right audience, but also for the websites where you want to show your ads. It lets you choose the category of websites that you want to display your ads on. This helps you show your ads only on websites that your target audience likes to frequent. Overall, Google provides advanced targeting options that help you control who sees your ads and where. And, it does so in a way that will help you get the best results out of your advertising spend. 3. Types of Google AdWords Display Ads There are four main types of ads that you can place using Google’s advertising suite. You can select one or more of these for your advertising campaign:
4. Different Ad Sizes and Formats There are four key ad formats, and for each there are several size options that you can choose from. Here are the four main ad formats that you should know about: Square and Landscape These ads have either equal width and height, or the width is greater than the height. The various ad sizes include:
Also, remember that the file size of your image ads should not exceed 150kb regardless of the file format that you use. 5. Keywords and Targeting Basics As we all know, Google search ads are based mostly on keywords, and keywords are the main targeting option. You choose the keywords that you'd like your ad to appear on. For the most part, you target your ads based on what people are searching. However, the Google Display Network provides a lot more targeting options beyond keywords. As these are image ads or video ads, keywords are not always the most important targeting factor. In fact, what matters here is the selection of platforms or websites where you want your ad to be shown. So, go through the various targeting options for Google display advertising before creating a campaign. These are covered in the next point. 6. Various Targeting Methods Here are the various types of targeting that you can do for your Google display advertising: Placement Targeting This allows you to select the platforms where you want to place your ads and is probably the most important targeting decision for Google display ads. You need to understand who your target audience is and which websites they are most likely to frequent. Then, you can make a selection of websites or apps where you want to show your ads to your target audience. You can choose to target industry-specific websites or websites based on special interests that match with those of your target audience. Topic Targeting This lets you select the pages where your ads will be displayed based on the topic covered on the page. This is the logical next step after you have selected the websites where you want to show your ads. Audience Targeting This allows you to select your audience based on demographics, interests, their online behavior, etc. There is a detailed list of demographics that you can use to filter and find the most relevant audience for your brand. Google Display Advertising also has the option of interest-based targeting that allows you to target people with specific interests. Overall, Google Display Advertising provides advanced audience targeting options to help you deliver your ads to the right people. Contextual Targeting This is basically the Google Display Advertising’s version of keyword-based targeting. Here you need to make a list of keywords that are most relevant to your ad content. Google AdWords also makes keyword suggestions based on your product or website to help you select the best keywords. Remarketing This allows you to target people who have had some past interactions with your business. It has a whole set of targeting options based on the type of interaction a user has had with your business. Creating a Google Display Advertising CampaignOnce you know the basics, you can go ahead and create your first Google Display Advertising campaign. 7. How to Set Up a Google Display Advertising Campaign For all of you who are not familiar with the Google AdWords interface, here’s a step-by-step guide to help you create a Google Display Advertising campaign.
The process of creating a Google Display Advertising campaign is fairly simple and the steps are self-explanatory. And, Google provides a lot of helpful resources to help you at each step of the way. Tips for Running Successful Google Display Advertising CampaignsNow that you know the basics of Google Display Advertising, let’s focus on how you can optimize your campaigns. Here are a few tips. 8. Use a Combination of Targeting Methods Given the various types of targeting options provided by AdWords, it would be a waste not to leverage all of them. Using a combination of targeting options can help you refine your selection and make your targeting more precise. You can also use different combinations for different target segments and ad groups to take your ad targeting to the next level. It can help you select an audience at a much more granular level. For example, you can choose people with a particular set of demographics who have a specific interest and live in a particular area. Using just one of the targeting options would not have allowed you that much precision over whom you want to display your ads to. 9. Try Managed Placements for More Control Over Ad Placements As discussed earlier, you can select the platforms where your ads are displayed based on a number of parameters like industry or topics. Using these options, you help Google AdWords to find relevant websites and show your ads, making the process very simple. However, if you want more precise control over your ad placements, then you can opt for the “managed placements” option. This allows you to select exactly which websites you want your ads shown on. Google might sometimes get it wrong and place your ads on irrelevant websites. Having manual control over the process makes sure that your ads are displayed only on relevant websites. This can help you get the highest return possible on your ad spend. This technique is also useful for marketers who have limited budgets. It is also good for first-timers to start with managed placements and then expand to the broader placement options. 10. Optimize Your Ad Copy in Text Ads You can optimize your ad copy in a variety of ways, including: Headlines Headlines are usually one of the first things that people see in an ad and should, therefore, be compelling enough to get clicks. Write something that people can relate to, and build excitement or curiosity. Essentially, your headlines should have something that gets people interested enough to click on the ad to learn more. Here are a few effective tips to write engaging headlines for your ads.
Apart from these tips, you also need to be mindful of the essentials like the headline length. You can use a headline analyzer tool to further optimize your headlines. Ad Content Your headlines are meant to attract people but it’s the actual ad content that will finally close the deal. It should be relevant, engaging, and compelling enough for people to take the desired action. Here are some quick tips to optimize the content, both text and visuals, for your ads.
Calls-to-Action Once you have attracted users and engaged them long enough for them to go through your ad content, it’s time to close the deal. The ultimate goal is to encourage people to click on your CTA and check out whatever you have in store for them. Whether your goal is simply to get more website traffic or to sell products, the success of an ad starts only when people click on the CTA. Therefore, your CTAs should be able to encourage people to take action. These are some of the best tactics for writing compelling calls-to-action:
11. Experiment With Different Ad Formats and Sizes Just like with the targeting options, it would be a waste not to try out the different Google display ad formats and size options to see which one works best. This is also needed because some websites support only 1-2 ad formats. Therefore, to maximize your reach, you should try out different ad formats and place them on different websites. Some websites, for example, might not support rich media or video ads, so it’s better to use image ads there. Some might only support text ads and you might not be able to advertise on those if you only have visual ads. Overall, try out all of the ad formats first and then filter down to the one that works the best for you. 12. Always A/B Test Your Ads This is a must for every advertiser, regardless of whether they are using Google Display Advertising or any of its counterparts. A/B testing your ads helps you optimize your advertising campaign and gain valuable insights for your future advertising strategy. From finding out what ad copy resonates with your audience the most to finding out which images get the most clicks, you can learn a lot by A/B testing. Another advantage of testing your ads is that it helps you refine your targeting. You can use different combinations of targeting options for different ad groups and see which ones get the best results. Wrapping it Up Use this post as your guide to create powerful Google Display Advertising campaigns that actually work. Source: https://www.spyfu.com/blog/google-display-advertising/
0 Comments
When it comes to creating epic content, sitting down and just writing something isn’t enough. It needs to be helpful, well-thought-out, and easy to find when people need it most.
When someone needs to find an answer to a problem they’re having, they often turn to Google to find the answer. If your content was created with data from Google, that helps your chances of solving their problem. So how do you create content that uses data from Google? By using one of Google’s own tools, Keyword Planner, to research exactly what people are searching for. Google’s Keyword Planner will tell you the terms people are searching for, how many times per month they’re searching for those terms, and how competitive those terms are. It has its limitations, which we'll cover later, and there are other solutions to cover those gaps. What does the Keyword Planner do? The Google Keyword Planner is a multi-functional, feature-rich tool that can help as a big part of your keyword search and planning needs. Whether you’re doing your first-ever keyword research or already have a list of keywords, this tool can help you. From there, you can take that information to craft incredibly useful content for your ideal customers. Here’s how to use Google keyword search inside the Keyword Planner to create epic content. Getting Started with Google’s Keyword Planner First thing’s first: To access Google’s Keyword Planner, you need a Google Ads account. But don’t worry — you don’t need to run any ads or even enter you’re billing information. Just follow the steps below. First, you’ll need to go to Keyword Planner's homepage.
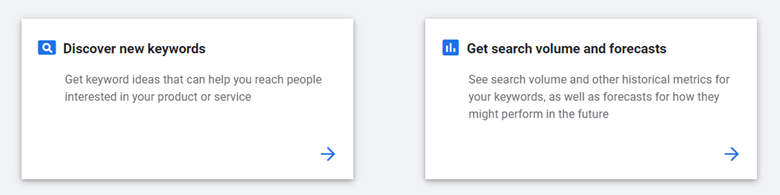
You’ll go through a few more screens that will ask you to confirm your business information. Click “Submit.” This won’t ask for credit card or billing info. At this point, you should be in your Google Ads platform. How to Get to The Google Keyword Planner Now you just have to open up Keyword Planner. Google hides this a little bit. To get to Keyword Planner, click on “Tools & Settings” in the top right of the Ads platform. And then click “Keyword Planner.” There’s one last step before you can start using Keyword Planner. On the next screen, you’ll be given two options. One that says “Discover new keywords” and another that says “Get search volume and forecasts.” Using the Keyword Planner for new Keyword Ideas Click the button that says “Discover new keywords.” Now the fun starts. You get to enter in your keywords that you want to target. In the box that appears on your screen, enter a keyword that’s related to your business. You simply need to type a topic, industry, niche, product, or anything that you want related keywords for. Whatever you type in the search box, you will find related keywords for that. Once you enter the search term, you will be directed to the results page which will show you a list of related keywords. You can use the reach and keyword filters mentioned above to sort through this list and find the best keywords for your business. You can also use the “Grouped Ideas” tab to find sets of related keywords based on a primary keyword. Keyword Planner will give you the ability to search 10 keywords at one time, but we suggest just focusing on one keyword at a time. Doing one at a time will make your keyword research much more organized. You can return to these steps with every new topic you'd like to cover. Once you're comfortable with the basics, you can move on to more helpful tips on what you can do with the Keyword Planner. 1. Filters to limit the audience you reach. Google Ads Keyword Planner is a brilliant tool that helps you with keyword research for your ad campaigns. However, if you simply type in a topic and look at the results, you will see more keywords than you can possibly check manually. And, even if you use keyword filters, this list will be too long. That is why you need to refine your keyword search, from the very start, to get a more relevant list of keywords. The Keyword Planner provides several filtering options that can narrow down the scope of your search. Here are some of the filters that you can use to refine and sort your keyword list: Language This filter will let you find keywords only in specific languages and will filter out the keywords in any other language. The search volume data for your keywords will also be specific to searches in a particular language. This feature is especially helpful if you have different copies of web pages in multiple languages. Using this, you can find language-specific keywords instead of using the same keywords for all. Location This provides you with search volume data for keywords from specific locations. You can also find keywords trends for a specific location, instead of global trends. These trends vary from location to location and you should narrow your searches to include only the regions that your business is present in. This filter is especially useful for local or regional businesses as they need to find location-specific search trends and keyword performance data. So, if you are focusing on local SEO, then you should use this filter. Negative Keywords Another way to narrow down your search results is to leverage negative keywords. These are basically the keywords that you do not want your ads to rank for. Negative keywords are very important in refining your keyword searches because you don’t want irrelevant or unrelated keywords. Sometimes, one word might have two meanings, one of which is completely unrelated to your business. If you use the negative keyword filter for such terms, then you will only find relevant and useful keywords for your campaigns. Search Network This filter decides where the data on keywords and search trends come from. You can choose the entire web or restrict it to only Google and Google Search Partners. Date This filter allows you to select a time period to restrict your search results. This means that you will see the keyword search volumes and trends for a specific period of time. 2. Filters to Limit Costs The next thing that you need to know about using Google Keyword Planner is the different types of keyword filters. These filters help you find the most relevant keywords for your business, from a list of keywords, and filtering can help you limit your costs. The Keyword Planner has several such keywords filters, here are some of the key ones: Average Monthly Searches This option can be used to sort and filter keywords based on their average number of monthly searches. Keywords with extremely high average monthly searches are more popular and difficult to compete for. It is also more expensive to bid for such popular keywords. Therefore, you should select keywords that have a good number of average monthly searches but are not extremely competitive. Using this filter, you can easily sort your keyword list and select the keywords that provide a perfect balance between popularity and competition. Organic Average Position This shows your page rankings for a particular keyword as compared to other pages ranking for the same keywords. This option is only available if your Google Analytics account is linked with your Google Ads account. Organic Impression Share This shows the percentage of times your page ranked for a keyword that it was targeting. This option is only available if your Google Analytics account is linked with your Google Ads account. Suggested Bid This helps you select the right keywords for your business based on the recommended bid for those keywords. Suggested bid is basically how much you would spend per click for an ad targeting that keyword. While selecting keywords for your ads, you also need to keep your budget in mind. You cannot select too many money keywords and overshoot your budget. Therefore, you should use this filter to find the best mix of keywords that are relevant and also within your budget. Ad Impression Share This is a very useful metric that shows you the share of people who actually see an ad for a keyword after searching for that keyword. This gives you an idea of how likely it is that your ad will be viewed if you target a particular keyword. Competition As the name suggests, this filter can sort keywords based on how difficult they are to compete for. The higher the competition, the more difficult it would be to rank for that keyword. A note about your keywords When trying to decide on a keyword to use, don’t go too broad. For example, if you run an ecommerce company that sells outdoor gear, don’t target the keyword “outdoor gear.” It’s too broad, and you won’t get any great ideas for content. Instead, make your focus a little narrower. Focus on specific product categories you offer, like “hiking boots,” “camping tents,” and “rock climbing shoes.” This will help narrow down the searcher’s intent so that you can actually create content that searchers are interested in reading. Tip: If you have a list of a few of these root keywords but aren’t sure which one to target first, enter all of those keywords into Keyword Planner at the same time to get the average monthly search volume for each root keyword. Then, start with the root keyword that gets the highest number of average monthly searches. 3. Your Plans Another feature of the Keyword Planner that you should know about is the “Your Plan” section. While doing your keyword search, you can add keywords to your plan and save those for later. You can think of these as temporary storage spaces where you keep adding any relevant keywords that you find during the course of your research. Once you have added sufficient keywords there, you can then analyze the performance metrics for each and make your final selection. The first time I saw this feature, I was hesitant to add anything for fear of disrupting the already-active Google Ads campaign that my account was tied to. You can move ahead with total assurance that using "Your Plan" will not automatically add these keywords to any campaign. Evaluate Keywords via Google Keyword Search The Google Ads Keyword Planner is not just for finding keywords but also for helping you make the right selection. The search volume and trends data can help you do exactly that. You can enter one or more keywords that you want to get this data for and simply look at the results. This option is best for people who already have a list of keywords and just want to check their performance metrics. A lot of marketers will already have data from website analytics tools about the keywords that they are ranking for. In this case, you do not need to search for new keywords but just analyze and refine your existing keyword list. Multiply Keyword Lists This is a very useful feature that allows you to upload two different keyword lists and multiply them. This forms different keyword permutations and combinations. Let’s say that you have a list of product-related keywords and one for locations. If you multiply the two lists, you will get keyword combinations with one product and one location. This is very useful when trying to find local-search keywords for your ad campaigns. The same can be applied to any two keyword lists to get different combinations of your primary keywords. After you have created a new keyword list with these combinations, you can always check historical and forecasted performance data for each. Get Forecasts on Click and Cost Performance Once you have found and added relevant keywords to your plan, you can get more advanced metrics and forecasts for those. This includes the number of clicks, impressions, cost, Average CPC, and other metrics. The best part is that it does not just show historical cost and click performance, but can also provide forecasts. This can help you determine whether a particular keyword is worth bidding for or not. Not just that, you can also see how a keyword has performed by devices and locations. 4. Keyword Bidding and Budget Allocation One key aspect of keyword selection is to analyze how much using that keyword will cost you and whether or not it fits in your budget. The Google Ads Keyword Planner provides information on average CPC, maximum CPC, and bid estimates. Average CPC is the average per-click cost that people pay for ads they want to rank for a particular keyword. The maximum CPC is the highest amount that anyone has paid to rank for a particular keyword. Now, you don’t necessarily have to make the highest CPC bid to rank well. In many cases, you can make an above-average bid. Keep in mind that your relevance and Quality Score of your site will play a part in how much Google weighs your bid to reach a higher spot and how much you will ultimately pay. The advertiser that outranked you on a particular search did not necessarily pay more. The more people there are bidding for a particular keyword, the more expensive the keyword. As mentioned earlier, high-competition keywords are not only expensive but are difficult to get a top ranking for. What this means is that your ads might not be displayed on Google’s first SERP or right at the top for highly competitive keywords. Therefore, you need to be smart about what keywords you bid for and how much. You can make an informed keyword selection using the planner and use Google Ads’ bid-optimization strategies to do the rest. Also, when making a final selection of keywords, check the total daily cost for all your keywords to get an idea about how much you might have to spend on a daily basis. Allocate your monthly ad budget keeping in mind your average cost and also keep some buffer in case an ad performs exceptionally well. 5. Keyword Competition As mentioned earlier, more competitive keywords are more expensive. But, how do you measure this competition? Well, while search volume is a good measure of competition, there is another metric that you can look at. The Keyword Planner actually provides a metric called “competition.” This categorizes the keywords based on how difficult it is to rank for it. There are three categories for this—high, medium, and low. This gives you a general idea about how tough it will be to compete for a keyword and helps you make the right selection. However, if you want more granular details of this metric, you can download this data in the form of a .CSV file. This way you will export all data to an Excel sheet where you can actually see the numerical values behind these (high, medium, low) categorizations. There might be hundreds of keywords that have medium categorization, but some would still be more competitive than the others. This data is helpful because it can help you prioritize between keywords that are in the same category. So, checking the competition score for keywords takes your keyword selection process to a whole new level and lets you make more informed decisions. When you are creating epic content that ranks, you can use these ratings (high, medium, and low) within the hub and spoke model. As you create competitive content that has a harder time ranking (high category), you can support it with internal links from relevant, topical content. Creating those pieces in the medium to low range might be easier on your workload and give you linking paths. Your longtail-focused, more specific content is an important part of supporting your broader content from an SEO angle, but it's also beneficial for your readers. 6. How to find keywords that will drive a lot of traffic The goal of keyword research is to find keywords that relate to the products or services that your website sells. Then you can use those keywords to create content that will attract your ideal customer. The best way to do this is to start by seeking out the keywords that have low competition but a high number of monthly searches. That combination will give you the best shot at outranking your competitors and getting a lot of organic traffic. For Google’s Keyword Planner, competition actually refers to the number of companies who are advertising on that keyword. Even though it’s a metric based on advertising, it’s still useful for content creation because highly competitive keywords not only have a lot of ads targeting them, but they also have a lot of people creating content for those keywords. To start finding low competition, high-volume keywords, you’ll first need to download the keyword ideas from Keyword Planner into a spreadsheet. Since we’ve already mentioned the ecommerce company that sells outdoor gear, we’ll stick with that as our example. Let’s say you work in marketing for that company, and you’ve decided to create content for people searching for the root keyword “hiking boots.” You’ve entered that keyword into Keyword Planner, and it has given you a list of 957 keywords. Not all of them are useful so you’ll need to download the list into a spreadsheet to find the best keywords. Now that the list is downloaded, you need to filter out all of the high-competition keywords. This returns a list of medium- and low-competition keywords. Let’s take it one step further and find the lowest-competition, highest-searched keywords. To do that, filter out all the keywords that have a search volume under 100. This number might change, depending on the specific keyword you’re targeting, but the point is to get rid of the keywords that get very few monthly searches. The remaining keywords are your “low-hanging fruit” keywords that you’ll want to tackle first. This list will be very small, and of the keywords that appear on this list, not all of them will be good keywords to build content around. There are six keywords left on this list, but only “men’s hiking footwear” and “hiking tips” are worth building content around. The others likely don't have the right search intent, which means you shouldn't waste time creating content for those.If you’re not sure of the search intent of a specific keyword, do a Google search with that keyword. When you look at the results, you should be able to tell if it’s a keyword that relates to your company. For example, the results for “women in boots” are definitely not related to outdoor gear. Back to our two useful keywords; we still have one more step to find a good content topic. Our next step is to find other keywords that can tie into these two. This will help give us a structure for an overall blogging strategy. Remove the filters from your spreadsheet, and manually sort it looking for keywords that fit your first keyword. You’re looking for commonalities here. How do other keywords fit into your original low-competition, high-volume keyword? For “men’s hiking footwear,” when we sorted through our keyword list, we noticed a number of keywords that could tie into this. We found a few different combinations of “boots or shoes.” That fits perfectly into our first keyword, and now we’ve got a working title for our first piece of content: “Men’s Hiking Footwear: Should You Buy Boots or Shoes?” We also found other combinations:
All of a sudden, we’re starting to build out a hub-and-spoke model for content creation. Our hub is going to be “Men’s Hiking Footwear,” and our spokes will be each of the secondary topics. The hub and spoke model is a great strategy to structure your content in a way that sets it up for success, regardless of how competitive your overall keywords are. Now, go back to the beginning, and repeat this same process with our other low-hanging-fruit keyword, “hiking tips.” Once you’ve done that, restart the whole process, but this time focus on keywords that are slightly more competitive. Keep repeating this process as many times as you can, and then switch your main root keyword to another product category. For example, once we’ve exhausted the “hiking boots” root keyword, we would switch and go after “rock climbing shoes” as our next root keyword. Epic content requires in-depth keyword research If you truly want to create epic content that gets a lot of attention and ranks highly in organic search, you need to take a strategic approach to it. Keyword research with Google’s Keyword Planner, or with another keyword research tool, is the first step to creating a strategy for your epic content. Keyword research takes a lot of time, but if you skip it, you’ll just be guessing at what type of content will rank well for your website. That’s going to lead to a lot of wasted time and energy. Source: https://www.spyfu.com/blog/google-keyword-planner/ What Is the Google Ads Keyword Forecast Tool? It’s one thing to know what’s trending now. That’s a valuable asset for any digital marketer. But what about what’s going to be trending tomorrow, or farther into the future? How do you even predict that? The Google Ads Keyword Forecast tool does just that. It’s an awesome option for anyone looking to up their SEM and SEO game by narrowing down future potential for any keywords or groups of keywords. According to Google, they update their forecasts on a daily basis, with data from up to 10 days past. This data includes market changes that occurred throughout this time. It also takes seasonality into consideration, so you’re not confused by natural market fluctuations. In short, Google Ads Keyword Forecast is a pretty cool tool. How (& Why) to Use the Forecast Tool The forecast tool is a multifaceted part of Google Ads, and it just goes to show how useful the Ads platform is as a whole. It goes well beyond today’s data and delivers insights for the near future. So what does this forecast tell you? The forecast tool will help you figure out how your keywords will perform in optimal settings. You can:
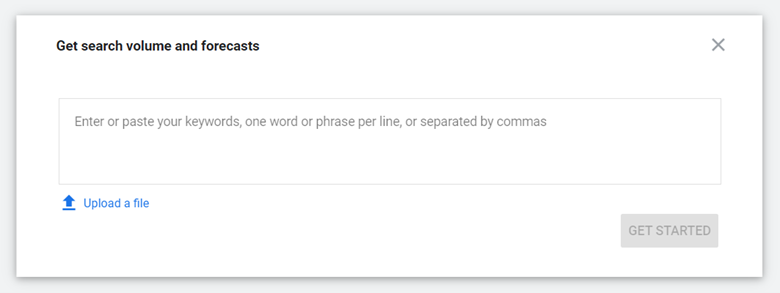
Your forecast has a date range, and you can change the time frame to see how it affects your forecast. There are two ways to see forecasts on Google Ads, so let’s break the Google Ads Keyword Forecast tool down for you, step by step. How to Use It for Forecasting Within the Google Ads Keyword Planner, you’ll find something called a forecast. Instead of clicking Discover new keywords, you’ll click Get search volume and forecasts. Once you’re here, you can enter an individual keyword or a group of keywords that are separated by commas or line breaks.
You can also upload a spreadsheet file to quickly transport keywords into the forecasting tool (as any SEO or SEM professional ought to know, there’s nothing wrong with a good shortcut!). Once you enter your keywords and click Get Started, you’ll come across a page with a few tabs. For the forecasting side of things, you’ll obviously want to stay under the first tab. Based on the keywords that you entered, you’ll see a selection of forecast data. Automatically, Google Ads tells you:
You can also add your own conversion metrics to tailor your forecasts to your brand’s unique marketing plan. This is an important trick for anyone who wants a nuanced forecast that’s perfectly fit for them. To do this, just click Add conversion metrics. In the end, you’ll be left with a pretty nifty graph and data chart that showcases future predictions (or forecasts) for your selected keywords. This helps you determine the best plan of action for campaigns to come, and even lets you know if you should adjust existing campaigns based on consumer queries and behavior. Keep in mind that the numbers you see associated with each metric is what you’re likely to achieve for your keywords or group of keywords based on your ad spend. These numbers will change if your budget changes, proving just how holistic Google’s approach really is. However, Google makes it very clear that spending more doesn’t necessarily equate to better conversions. When you’re done, take one or all of these steps:
Is This the Only Way to See Forecasts On Google Ads? Short answer: No, it’s not! Long answer: There’s another way, and you can find it by clicking Discover new keywords instead of Get search volume and forecasts at the start. When you use Discover new keywords, you can:
But in addition to these, you can also see a performance forecast once keywords are on your plan. As an optional measure, you can create a new campaign based on positive forecasts. Or, you can use them to beef up your existing campaigns. If you want to add keywords to your plan from Discover new keywords so you can forecast their performance, you can follow a few simple steps:
Ready to get started with your Google Ads Campaigns? Follow CPC Ninja on Facebook. If you're interested in getting an agency that could help you get better ad results, shoot us a message. Want to improve AdWords click-through rates? Getting your AdWords campaign up and running is pretty easy. But, if you don’t optimize your ad campaigns well enough, your click-through rates could be low, making your entire AdWords campaign less effective.
In this article, we’ll show you how to optimize your AdWords campaign to boost click-through rates. 1. Use Ad ExtensionsAdd extensions are additional information you can include in your ads to entice people to click on your ads and make them choose your business over your competitors. Some of the useful ad extensions are: Call extension: If you’re promoting a service using AdWords, adding a call extension could significantly increase your click-through rates. People can tap or click a button to call your business directly from your ads without having to visit your landing page. Review extension: Attract new customers to your store by adding a social proof right in your ads using review and rating extensions. Price extension: The Price extension appears below your text ad, giving you more space to tell more about your offering. 2. Optimize Your Display URLA display URL is a web address that your prospects see in your pay-per-click ads. It gives people an idea of where they’ll arrive after they click your ad. When creating an ad campaign, keep in mind that your actual landing page URL does not have to match your display URL, but should be in the same domain. A few ways to optimize your display URL to increase ad relevancy are: Use a keyword: Include a keyword in your display URL. Google bolds the keyword in your display URL when it matches the search query. Use a call to action: Hyatt, for example, uses the call to action Book now in their display URL to encourage clicks. Make it readable: Use camel case and hyphens in your display URL to make it more readable. 3. Personalize Your Ad CopyAdWords allows you to personalize your ads to a great extent to match your ads with the search query. If you’re a local advertiser, you can use geo-customizers to dynamically update your ad based on the searchers’ physical location or location of interest. You can also personalize the copy based on the following dimensions: device, time, audience, gender or age. 4. Create Tightly Themed Keyword GroupsGoogle AdWords allows you to include multiple keywords into your account and ad groups. While this helps you win a chance to reach your ads to your target customers, at times your ads won’t contain the keyword that people were searching for, which would adversely affect the click-through rates and quality scores. To increase the likelihood of your keywords to appear in your ads, you might use tightly grouped themes or keywords into smaller ad groups rather than a broader ad group. 5. Use a Countdown TimerFinally, your ad clicks won’t mean anything if those visitors don’t convert on your site. Creating a sense of urgency is a great tactic to persuade users to act quickly. Urgency works because it causes people to suspend deliberate thought of procrastination. Obviously, no one likes to miss out on a cool offer. If you want to boost clicks on your ads by creating a sense of urgency, AdWords allows you to insert a countdown timer in your ads to highlight your upcoming events. The ads with countdown timer are proven to perform at a significantly higher rate than other copy. After clicking on your ads, your prospective customers will expect the same tone and message on your landing page as well. If you’re using a countdown timer in your ads, it’s in your best interest to use a similar timer on your landing page as well to meet your prospects’ expectations and boost conversions. Using a countdown timer is a great strategy for eCommerce stores to boost ad clicks and conversions. You can use a countdown timer to promote…
We hope this article will help you improve the click-through rates of your next AdWords campaign. Google Ads is arguably one of the most misunderstood platforms for paid advertising. Many business owners promote their wares with sponsored posts on social media sites like Facebook, but underutilize Google Ads, despite the unique opportunity it offers to advertise their products and services directly to people actively searching for them.
Google puts a large breadth of advertising tools at your fingertips. It also gives you access to users of the world’s two largest search engines—Google and YouTube, respectively—and a network of millions of websites to advertise on. Unfortunately, Google Ads has a complicated interface and a steep learning curve. If you don’t know what you’re doing, you can end up targeting too broad of an audience and spending money without turning a profit. But everyone has to start somewhere, and whether you plan on managing your own Google advertising or outsourcing it to an expert, it’s best to begin by learning the necessary terminology and knowing not only the campaign and ad types available to you, but what you can realistically expect from them. That way, you’ll understand exactly what the platform can do for you. Why use the Google Ads platform?Google Ads has a lot in common with many other paid advertising platforms. With it, you can:
1. Search adsConsumers generally use search engines—unlike social media—with a specific intent in mind: to search for answers, get solutions to their problems, or find specific products or services. This makes Google a powerful marketing channel for a variety of businesses. You can inform how you advertise on Google based on the average volume of monthly searches for a given query, the estimated cost you would pay per click, and other data Google makes readily available. You can run search ads that promote your products and services directly in the search results of a specific query and even narrow your targeting to users in a certain geographical area. Say you’re selling plant-based protein powder. More than 200,000 people search for “protein powder” on Google every month, but there are far fewer searches for “vegan protein powder.” Google will let you bid (more on this below) to advertise your brand on both of these phrases individually, but the more specific search term likely will convert better because it’s more relevant to your product. You can create text ads, which display in search results marked with the word “Ad” in a small box, or Google Shopping ads, which surface key purchasing information, such as product photos, prices, and ratings—something that makes them perfect for many ecommerce brands. You can see both text and Shopping ads in action below. 2. Google Display NetworkYou can also advertise your products or services to potential customers through the Google Display Network. Display advertising gives you the option to reach people outside of Google’s search engine results, through text, image, and video banner displays that appear as users browse the web, use apps, or watch videos. While many advertisers turn to Facebook for their display advertising, Google is also a viable option. The Google Display Network reaches 90% of all internet users around the world and consists of ad space on more than 2 million sites and 650,000 apps. Visit any news site and you’re likely to see Google display ads at the top, in the sidebar, or even throughout the content itself. 3. YouTube adsThe Google Ads platform also lets you advertise on YouTube, which is owned by Google. Technically, YouTube is just one site in the Google Display Network but, measured on its own, it is the third most-visited site on the web, after Google and Facebook. Users watch more than one billion hours of YouTube videos a day. That makes for a lot of opportunities to engage potential customers. You’re probably familiar with the pre-roll ads that play before YouTube videos, but there are also banner and overlay options. As you can see, Google offers a variety of ad types. But before you choose between text, image, or video, you need to understand where your ads will be shown and who will see them. How the Google Ads auction worksMany of the campaign types available through Google Ads operate on an auction system. Advertisers compete for a position or “rank” on the search engine results pages by bidding (usually) on clicks. The amount you bid and how you set up your keywords will determine your placement in relation to other bidders. However, the highest bidder doesn’t necessarily win the top spot; relevancy is also a determining factor. Google wants to show ads that are useful and relevant to its users, and you want to advertise to relevant users who are searching for your business or terms related to what you’re selling. So Google assigns an Ad Rank based on various factors, such as the relevance of your ad copy and ad format to the keywords you’re buying, the webpage you’re sending visitors to, and more. As an advertiser, the more relevant your business is to the terms you’re buying, and the more relevant your ad messaging is to users searching for those terms and the page you’re sending them to, the cheaper it will be for you to rank for that traffic. Before you dive headfirst into the world of Google Ads—or hire a professional to manage your marketing on the platform—there are some key concepts and campaign types you’ll need to understand. Google Ads terms and conceptsPaid marketing—Google Ads in particular—comes with its own vocabulary of terms and concepts. Here’s a glossary you can reference if you encounter a term you’re unsure of: Paid marketing terms to learn
Keep in mind there will always be trade-offs and other dependances to consider. For example, certain campaign types sacrifice segmentation—bundling various audiences together, making it hard to isolate specific high-performing groups—but will be easier to set up yourself or through an app or integration with Shopify. Other campaign types might be harder to execute successfully, requiring more manual set up and ongoing optimization, especially if certain audiences or keywords are highly competitive. These campaigns will require more technical expertise, time, and money. For this reason, any ranges or estimates given here are meant to serve as guidelines. Your actual cost per click or expected return will depend on many variables, such as how well your website converts, your average order value, and how much scale there is for a certain type of keyword or audience. We’ll outline each campaign type according to the following information:
Not all businesses will be able to take advantage of all campaign types, and some of the more competitive campaigns often require a lot of human capital and time to manage. They can also be expensive, especially in the beginning. Note: Since Bing and Yahoo! share similar features with Google, many of the campaign types below can also be run on those platforms. The Google Ads playbook: 13 campaign types1. Branded search
You might not think to bid on your own brand name, especially if your site already appears organically at the top of search results, but doing so lets you promote specific information (using Google’s ad extensions) and set the exact page where you want people to land. It also protects you from competitors who might bid on your name or other branded keywords. CPCs for branded search generally will be lower than for any other search campaign, since your URL and your ads will be highly relevant to users who search for you. At the same time, be wary of your ad appearing for similar but irrelevant keywords. In the example of Apple advertising iPhones, you would exclude keywords such as “apple picking” or “apple cider,” or even “how to update my Apple iPhone” and narrow your targeting using the appropriate keyword match types and negative keywords. Since your ceiling for sales from branded search depends on how many people are actually looking for you, branded search campaigns can complement brand awareness campaigns. A pop-up shop or a viral Facebook video, for example, can translate into more searches for your brand name. Ease of implementation: This type of campaign can be hard to implement if you’re not familiar with search engine marketing. Agency or in-house resources may be required. However, branded search isn’t that labor-intensive to manage, so make this a priority if you can. 2. Non-branded search (generic)
The goal of this campaign is driving new visitors and new customers to your site as efficiently as possible. But these campaigns can also have a positive ROAS for advertisers and a massive amount of potential scale. Keep in mind that the true value of a customer is not their initial purchase but their lifetime of purchases from your brand. Ease of implementation: As with all search campaign types, this one can be difficult. These campaigns require a lot of human resources to manage and test your creative and landing pages, plus a lot of money to drive results. It’s best to hire help to ensure these campaigns are managed correctly. 3. Non-branded search (niche)
If your business and products are a fit for niche marketing, then this campaign type is worth exploring. Niche marketing, even outside of the context of Google Ads, gives brands a much easier time of getting traffic and, potentially, a positive ROI, because it offers a specific audience that’s easier to identify and focus on. Niche non-branded search often is lumped together with generic non-branded search. But, for the reasons given above, it makes sense to segment this traffic in its own campaign and discuss it separately. If you sell third-party products, you can also apply this campaign type by bidding on the specific branded keywords associated with them. When buying these keywords, you can even use these brand names in your ad creative as long as you link directly to a landing page that has those products visible. Ease of implementation: Similar to other search campaigns, this campaign type isn’t easy to undertake and will require appropriate resources to set up and maintain. If you don’t understand keyword match types and how to build and optimize search campaigns, ads, and landing pages, we would recommend hiring an expert who does (more on that later). 4. Competitor search
Stealing traffic from your largest direct competitors’ keywords sounds like a smart strategy, but it can also be a relatively expensive one because, in this case, you, a competing brand, aren’t the most relevant thing searchers want to see. Typically, this strategy is employed by brands that can justify the higher costs of acquiring a new customer who might have a relatively higher average order value or lifetime value. Otherwise, you may experience little success with this strategy. If a brand isn’t buying its own traffic or doesn’t have a lot of brand loyalty among its customers, and if your product is an equal or better alternative, this could actually be a very profitable campaign for you. (Part of the reason we highly recommend buying your own branded terms is to prevent this type of disruption from a competitor.) Note: You shouldn't use dynamic keyword insertion in ads when buying your competitor's branded keywords, nor can you use their name in your ads if you don't sell their product on the page you drive traffic to. Ease of implementation: As with all search campaigns, this one is not easy to do and could be very expensive. You would want resources dedicated to managing this. 5. Google Shopping (branded)
In terms of new customer acquisition as an ecommerce business, this is at the top of your list of campaigns to try. Users who specifically search for your brand are more likely to convert, so if you’re able to set up branded Shopping as a separate campaign, you can maximize your traffic from this source and be able to budget more effectively. Otherwise, Shopping campaigns will include both branded and non-branded traffic by default. Without a segmented campaign strategy, there will always be more non-branded than branded traffic, and the majority of your budget will likely be spent on non-branded terms that are less likely to convert. That’s why, if you can (and have the traffic to take advantage of it), it’s worth separating branded traffic into its own Shopping campaign. Ease of implementation: Shopping campaigns generally are easier to set up than search. To create a working product feed Google can pull from, you either can install Google channel for Shopify or set things up manually in the Google merchant center. You’ll need to create individual campaigns for branded and non-branded traffic, apply negative keywords, and prioritize keywords to exclude your ads from displaying for certain queries to isolate branded search traffic. 6. Google Shopping (non-branded)
Non-branded shopping campaigns work similarly to non-branded search campaigns. If you have the budget, they are something that almost always makes sense for ecommerce businesses to try. If you don’t have any branded products, a normal shopping campaign essentially will be a 100% non-branded campaign. Ease of implementation: Separating out branded and non-branded traffic requires a bit of set up, but once done you can have separate non-branded Shopping campaigns and dedicate a specific budget for each. 7. Retargeting (text, banner, video)
Retargeting is a strategy that lets you continue to reach these visitors off-site, often at a lower cost, to bring them back to your site through different, more specific messaging. Retargeting is a powerful feature that helps you turn first-time visitors into return visitors and, ultimately, into first-time buyers. It can also be used to generate repeat purchases by advertising to existing customers. For example. you can apply retargeting to YouTube with video ads for users who have visited your site. This makes a stronger second impression and can be very powerful if bundled into an existing strategy. Unlike with the other display campaign types covered above, where your ads appear matters less since you’re targeting specific users that will recognize your brand no matter what site it appears on. However, maximizing your retargeting efforts will involve a lot of additional segmenting based on users who have more recently visited your site, explored your product pages, or abandoned their carts. Simply targeting all users who have been to your site in the past 30 days might result in you reaching buyers without any intention of purchasing. Similar to how there can be a wide range of search terms to consider for non-branded search, how you target a user who saw a specific product and added it to their cart in the past 24 hours will be different than a user that was on your homepage 40 days ago. Your expectations should vary accordingly. Ease of implementation: This type of campaign isn’t too difficult to set up if you know how to create negative audiences and load ads and targeting into Google Ads. However, you will want to dedicate resources to maintain it, since the goal with retargeting is to create a profitable mechanism you can use to convert past visitors into customers. Also, If you want to use YouTube retargeting for video ads, you'll need your own channel with video assets uploaded to YouTube. 8. Display ads (topics and interests)
While you have a few targeting options at your disposal here, the broadest will be based on topics and interests, which can range anywhere from autos and vehicles to travel to home and garden. With topic-based targeting, your ad will be served on any of the sites belonging to that category in the Display Network. With interest-based targeting, your ads will be shown to users who have recently started researching those topics using sites in the Display Network. If you’re considering these types of display campaigns on Facebook, it might make sense to put some of your ad testing budget into Google’s equivalent. Ease of implementation: Setting up a display campaign is relatively straightforward, but you’ll need to exclude certain keywords and placements (using negative keywords and negative placements) to really optimize its effectiveness. 9. Display ads (contextual)
The majority of a user’s time online is spent consuming and engaging with content, not searching on Google. Because of that, getting in front of users as they engage with content relevant to your product or service is always a potentially viable approach to test and measure lift. While not necessarily a priority over higher intent search campaigns, the ability to showcase your ads (image, text, video, etc.) to potential users without having to pay unless they click is a great opportunity. Contextual campaigns are a great way to start on the Display Network because they let Google show you niche sites that might be available for you to directly target your audience on. Note: You can get contextual campaigns and the Display Network as a part of your other search campaigns. However, we would always advise turning the Display Network off for search campaigns and turning search off for display campaigns. They work very differently, and so should be separated and budgeted as such to give you more control over how much money is spent on what effort. Ease of implementation: Generally, if you understand how to group a few contextually relevant keywords and set up an ad through Google, you could start running this campaign. It’s not as hard as search ads, though there’s also no app or direct integration to automate set up. 9. Display ads (managed placement)
Typically, you would execute this type of campaign after identifying the specific website placements that were effective in your contextual or topic/interest display campaigns. Ease of implementation: Generally, this is an easier campaign to set up if you have some experience and can navigate around the Google Ads platform. 10. Google Smart Shopping
This campaign type chooses which products to advertise, how much to bid, who to target, and which creative to show. Shopify’s integration with Google Shopping lets you pull your products and product feeds automatically into these campaigns—you can even launch directly from Shopify using Marketing in Shopify. Your performance here will depend on how many users search for your brand, products, product categories, or branded keywords. The amount of retargeting you can do and the branded traffic you can drive through Shopping ads also depends on the search volume for your branded keywords and the size of your retargeting audience (i.e. how many people have visited your site already). Ease of implementation: Smart Shopping represents a very easy way to get involved with Google advertising, whether with Shopping or retargeting ads. If you see success, there may be a greater opportunity to transition to a more segmented manual campaign strategy in the future. Marketing in Shopify: Grow your business with Facebook and Google Ads Marketing in Shopify is a new place to help you create, launch, and measure campaigns. We’ve streamlined the process to make running a successful Facebook carousel ad or Google Smart Shopping campaign easier than ever. Run your first campaign on Shopify11. CRM (search, YouTube, Gmail)
This audience is highly qualified, so you can expect a great ROI if you execute your campaign properly. The one caveat is that you need to have an established customer base (i.e. thousands of emails), so this approach will not work for newer merchants. These are hyper-targeted campaigns that leverage the information you have about your customers in your CRM. You can extend specific messaging to different segments of customers, targeting placements in Gmail, YouTube, or search. About Customer Match Rate: Not every email you upload will match with Google’s database. For example, if you upload a list with 4,000 emails, Google may only be able to match 2,000 of them. Gmail addresses are more likely to have a match, but you can expect a sizable portion of your list won’t be targetable. Ease of implementation: Not only do you need an established customer base to execute this campaign, you would also need the knowledge and experience to segment your list to speak to different customers differently If you have those elements, navigating Google Ads to upload your seed list and set up your ad types is pretty manageable and well-documented online. 12. Similar audiences
Google Ads is able to take similar interests shared from your seed audience and match your ads to target other users on the Google Display Network who also share those interests.. Ease of implementation: We recommend trying intent-based campaigns first, but if you’re trying similar audiences on Facebook, this might also serve as a viable option to test and review performance. 13. Dynamic search ads
There’s no out of the box segmentation in this campaign so, like other campaigns that bundle together your traffic, we don’t recommend this as something to keep forever and scale but rather as a starting point to eventually segment manually as you gather performance data. Ease of implementation: This is a great quick and easy way to get a search campaign online. However, while it’s easy to implement, there’s a large possibility dynamic search campaigns will contain irrelevant keywords that are on your site but that you would never manually buy to gain traffic. Budgeting: always-on vs. testing campaignsWith any form of paid marketing, budgeting is an essential consideration that raises many questions. How should you set your budget? How long should you test a campaign/ad? How can you even tell if a campaign is achieving its intended purpose? To answer these questions, you need to understand the two main categories of campaigns you’ll be running. Always-on campaigns focus on profitability and high potential sales from shoppers who show intent to buy your brand/product/service. These are campaigns you’ll want to run continuously to capture your lowest hanging fruit. They include:
For example, if you have only $10 a day to spend on marketing (or a fixed budget that you could spend 100% of), an always-on campaign might be the best use of that money—unless you have specific customer acquisition or awareness goals on which that money would be better spent. Beyond converting your warmest audiences, you can also spend money to drive new customers to your site or drive awareness about your products/services to a specific audience. That’s what testing/flexible campaigns focus on—driving new customer acquisition, awareness, and engagement with your site and products. They include:
If you’re managing your own Google ads, be mindful of your level of expertise with all of the above. You can get set up quickly with Google Smart Shopping or dynamic search campaigns to get you started, and then reassess what is best for your brand based on all the possible options and best practices explained above. This always-on vs testing approach to budgeting can also be applied to other forms of paid marketing, from Facebook to influencer marketing campaigns, to decide how much budget to allocate and where. How to hire help to manage your Google AdsIf you feel overwhelmed, you’re not alone. Many entrepreneurs who can’t afford the time or money it would take to successfully learn and manage their own Google advertising, outsource it to agencies or experts who specialize in paid advertising. Here are some things to keep in mind when outsourcing your Google Ads:
Final thoughtsWe won’t sugarcoat it—succeeding with Google Ads isn’t easy. There’s a lot of nuance to each ad campaign type, with even more campaign types and variations that weren’t explicitly covered above, not to mention attribution, which is a key topic for another article. But the Google Ads platform has benefits for any ecommerce business willing to figure out how to advertise to its massive user base based on search intent and a variety of other targeting options and placements. Hopefully, you now have a better understanding of what’s possible on the Google Ads platform, what to expect from the different campaign types available, and how they can work together with the rest of your marketing engine. Whether you invest the time and money into learning how to run your own campaigns, or lean on an agency's or expert's services, getting to know the platform and your options is a great first step in the right direction. This post was originally published by Shopify Blog. Facebook Ads and Google Ads are the two top players in PPC advertising. Although the two have a lot of common ground, no two platforms are exactly alike and no matter how small these differences are, these could be your determining factors as to what platform your business should invest in. Facebook Ads vs. Google Ads: What's the difference? Before we get into specifics and strategies, you should know where your money is going and what it will be used for. Facebook and Google are both advertising platforms working on a pay-per-click basis. Upon creating an ad on either, you enter a bid on how much you want to pay for an ad space. Then, you will be charged a certain amount of money whenever someone clicks on your ad. Google Ads is paid search. Paid search means that you're paying to have your listing featured on a search engine result page (SERP). With paid search, your ads are placed on top—at the exact moment a consumer needs you— of a SERP based on the keywords you have made a bid on instead of a specific audience based on interests and demographics. Facebook Ads, on the other hand, is paid social advertising. With the continuous development of the platform, businesses get a hard time putting their brands organically in front of consumers over the years. With Facebook Ads, you can get your products and services in front of potential customers—even when they don't need it yet—in a faster and easier way. Awareness or Conversions? If you are looking into introducing a new brand to the market or simply wanting to expand your customer base, Facebook Ads might be the right medium. If you are a seller of retail items or services, launching ads on Facebook might just be the best marketing effort to grow your business. Facebook Ads are passive. These are displayed even without a user's need for a specific product or service. However, this type of ads spark interest that can eventually convert a user to a customer in the long run. Once your ads have been shown and awareness has been established, users will more likely resort to your brand once their need for it arises. On the contrary, Google Ads are active ads. This platform has been proven to work effectively because people are searching for something that they need at the exact moment. Thus, the high chances of getting a conversion rather than passive advertising. For example, if you need a tailor, you are probably going to "Google" one in your area rather than scroll on your Facebook feed in hopes of finding one. Services work well with this platform since customers are already looking the business instead of the other way around. Which one works best?
I would say that depends on your personal preference. There is no specific situation where in one platform is better than the other. It is important for businesses to know their options and goals before investing into either platforms in order to get desirable and aligned results. While both Facebook Ads and Google Ads prove to be excellent choices for PPC advertising, they are also found to work best when they are used together. If you'd like to know more about Google Ads and other marketing strategies, you may follow CPC Ninja on Facebook. If you're interested in getting an agency that could help you get better ad results, shoot us a message. In the last few months, the world seemed to have slowed down, if not entirely put to a stop. Borders and establishments were closed, people were contained, and lockdowns were implemented causing some businesses to shut down and permanently cease operations.
The outbreak of Covid-19 has forced us to see things on a different aspect and quickly adapt to the changes the pandemic has bring forth. As marketers and business owners, we often ask "how permanent are these changes and how do I keep the business afloat despite them?". If you were to take things on a more optimistic light, the pandemic has given us a gift: the evolution of digital marketing. Nowadays, you can see people practically stuck to their laptops, tablets, and phones browsing almost 24/7. Meaning, this is an opportunity for us to sell to them and we definitely should take advantage of it—through ads. If you're a business owner who is currently running Facebook Ads, then investing on Google ads might be a game-changer for you! Here are 5 good reasons why you should put your money on a Google Ads basket: 1. The traffic is ready for you. These days, "Google it" has become one of our common routine when we are trying to search for answers. Most often than not, people who are searching for services on Google are practically the ones who are "ready to buy" or "already close to buying". To compare it with Facebook ads, a user comes across your shampoo ad, stops to read, maybe clicks the ad to know more, and saves it for later should she need a different shampoo next month or next year. But that doesn't mean that it's a waste of ad spent. With Google ads, a user will first have to search for the "best shampoo for dry hair" or anything of that sort before your ad pops up on her screen. She then clicks it, thinks it's a good shampoo, adds the product to her cart, and BAM! Ka-ching, ka-ching! You got to close a sale on a significantly shorter period of time. Timing is the best thing Google Ads can offer that no other advertising platform can. With Google, your ads will be pushed out to the right people at the right moment. 2. You get what you pay for. Unlike Facebook, Google charges you for the number of clicks your ad incurred instead of the number of times it was shown on users' screens. This is definitely a bang for your buck because you do not necessarily have to pay for people who see your ads and don't click them. Although the average cost-per-click on Google may be a little higher than on Facebook, you can be reassured that you are getting quality and strategic clicks. With more quality clicks, come more quality leads, and more sales eventually. 3. You have COMPLETE control over your ads. I am not exaggerating on this, but yes, hats off to Google for giving advertisers the total freedom to plan and play with their ads. With Google Ads, you'll get the liberty of bidding on your desired keywords, with your desired budget, and your desired placements. How does it work? Simple. Once you set up a campaign with Google, you can choose the keywords and maximum cost-per-action (CPA) that you think will best push out your ads to the right people at the right time. For example, I only chose the keywords "best shampoo for dry hair" and "dandruff shampoo" for my ads with a maximum CPA of $5. Google will then start pushing out my ads only to the people who are searching for the keywords I have placed a bid on. What if there is competition? Let's say there is another shampoo brand bidding on the same keywords with a max. $3 CPA. Of course, my ads will be pushed out first since I bid $2 higher than them. Do I have to pay $5 then? No. Google will only charge me $3 for each click since I outbid my competitors at a maximum of $3 CPA. 4. You are in for a BIGGER competition. You may think that this is a disadvantage, eh? Well, I guess that depends on your preference of seeing things. Any starting business have dreamt of being side-by-side and in competition with bigger and more well-known brands, right? Google can make that dream come true! With Google, you will have the opportunity to work your way to make it to your competition's placement ranks or even better them at it with just the right keywords and strategic budget. Unlike in SEO, it can take months or even years to get your business rank high in Google. On the other hand, Google Ads can make your business #1 within hours with just the perfect keyword and budget combo! 5. It complements and boosts your other marketing efforts. As a business owner or an advertiser, you may now be thinking of investing on Google Ads and completely putting your other digital ads to a stop. DO NOT DO IT! That would be a total mess and a marketing sabotage! Facebook and Google ads work best when they are done together. One important strategy that may help boost the performance of your ads is build brand awareness with Facebook and close deals with Google. Simply put, when users see your ad on Facebook, they will somehow have an interest in your offer but still do not know what your brand is about. The next thing they would want to do is conduct a little research on Google and that paves the way for you to convince your warm audience to buy or take action. The key here is coherence. When a same offer or message is conveyed across different channels, taking action is going to be more likely and closing deals will be much easier. That way when someone sees your Google ad after seeing your Facebook ad, they will know what to do and where to click. In closing, the uncertainty of the future for marketing is understandable. Collaborative efforts on different marketing platforms could either be your business' holy grail or not, depending on how you see it and work your way around it. But one this is for sure, this too shall pass and as marketers, with every crisis comes an opportunity waiting to be taken. If you'd like to know more about Google Ads and other marketing strategies, you may follow CPC Ninja on Facebook. If you're interested in getting an agency that could help you get better ad results, shoot us a message. |
|